Blood Cancers
Blood cancer is a group of cancers which affect blood cells, blood forming tissues or the immune system cells.
Main types:
- Lymphoma
- Leukemia
- Myeloma
Lymphoma and Leukemia are the most common Blood Cancers
Blood Cancer that affects the immune system and especially the lymph cells which are type of the white blood cells.
Types of lymphoma
There are 2 kinds of lymphomas:
- Hodgkin lymphoma
- Non-Hodgkin lymphoma
They behave, spread, and respond to treatment differently, so it’s important for you to know which one you have.
Hodgkin lymphoma
- Hodgkin lymphoma can start almost anywhere, most often it starts in lymph nodes in the upper part of the body. The most common sites are in the chest, neck, or under the arms.
- Hodgkin lymphoma most often spreads through the lymph vessels from lymph node to lymph node.
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma
- Non-Hodgkin lymphoma is a cancer that starts in the lymphatic system in blood cells called lymphocytes. This cancer can be almost any place in the body.
- Age: People can be diagnosed with Hodgkin lymphoma at any age, but it is most common in early adulthood (especially in a person’s 20s) and in late adulthood (after age 55).
- Gender: occurs slightly more often in males than in females.
- Family history: Brothers and sisters of young people with this disease have a higher risk for Hodgkin lymphoma.
- HIV infection: The risk of Hodgkin disease is increased in people infected with HIV, the virus that causes AIDS
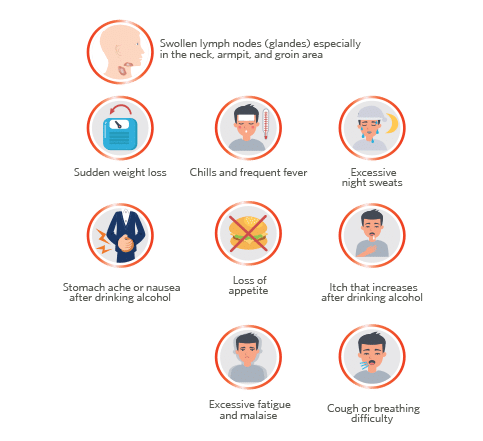
The most common symptom of Hodgkin lymphoma is a lump in the neck, under the arm, or in the groin, which is an enlarged lymph node.
Some people with Hodgkin disease have what are known as B symptoms:
- Fever (which can come and go over several days or weeks) without an infection
- Drenching night sweats
- Weight loss without trying (at least 10% of body weight over 6 months)
Other possible symptoms of Hodgkin lymphoma include:
- Itching skin
- Feeling tired
- Loss of appetite
Sometimes the only symptom might be feeling tired all the time.
- Age older than 60 years of age
- Men are at higher risk
- Exposure to certain chemicals and drugs: such as benzene and certain herbicides and insecticides (weed- and insect-killing substances) may be linked to an increased risk of NHL, Some chemotherapy drugs used to treat other cancers may increase the risk of developing NHL many years later. For example, patients who have been treated for Hodgkin lymphoma have an increased risk of later developing NHL.
- Radiation exposure: Patients treated with radiation therapy for some other cancers, such as Hodgkin lymphoma, have a slightly increased risk of developing NHL later in life. This risk is greater for patients treated with both radiation therapy and chemotherapy.
- Weak immune system as in AIDS and organ transplant patients
- Autoimmune diseases, in which the immune system attacks the body organs
- Specific viral and bacterial infections
- Body weight and diet: being overweight or obesemay increase your risk of NHL. Other studies have suggested that a diet high in fat and meats may raise your risk.
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) can cause many different signs and symptoms, depending on the type of lymphoma and where it is in the body. Sometimes it might not cause any symptoms until it grows quite large. Some common signs and symptoms include:
- Enlarged lymph nodes
- Fever
- Sweating and chills
- Unexplained Weight loss
- Fatigue (extreme tiredness)
- Swollen abdomen (belly)
- Feeling full after only a small amount of food
- Chest pain or pressure
- Shortness of breath or cough
- Severe or frequent infections
- Easy bruising or bleeding
There is not a specific way to prevent Lymphoma. However, avoidance of HIV infection or chemical and radiation exposure may reduce the chance of having Lymphoma.

- Leukemia is a cancer of the early blood-forming cells. Most often, leukemia is a cancer of the white blood cells, but some leukemias start in other blood cell types.
- Leukemia is often described as being either acute (fast growing) or chronic (slow growing).
- Myeloid leukemia: Leukemias that start in early forms of myeloid cells – the cells that make white blood cells (other than lymphocytes), red blood cells, or platelet-making cells (megakaryocytes) (also known as myelogenous leukemias).
- Lymphocytic leukemia: Leukemias that start in immature forms of lymphocytes are called lymphocytic leukemias (also known as lymphoid or lymphoblastic leukemias).
There are 4 main types of leukemia:
- Acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL). ALL is more common in children than in adults.
- Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). CLL mainly affects older adults.
- Acute myeloid leukemia (AML). AML is most common in older people.
- Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML)
The risk factors that put individuals at higher risk of having Leukemia are:
- Exposure to high level of radiation
- Smoking
- Exposure to Benzene which is frequently used in chemical industries and it is in the cigarettes smokes and car’s fuel (gasoline)
- Specific medications used to treat Cancer
- Specific types of bone marrow diseases
You should consult your doctor immediately if you have any of the following symptoms in a persistent (chronic) manner:
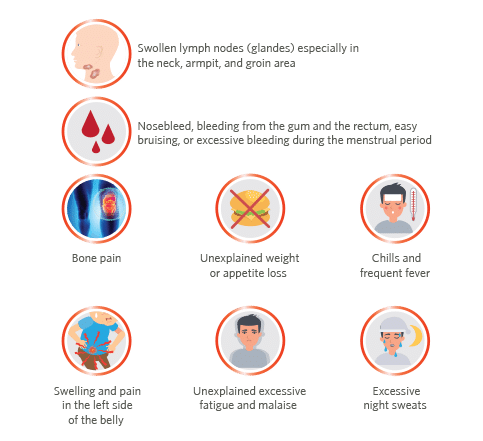
- Swollen lymph nodes (glandes) especially in the neck, armpit, and groin area
- Nosebleed, bleeding from the gum and the rectum, easy bruising, or excessive bleeding during the menstrual period
- Chills and frequent fever
- Excessive night sweats
- Bone pain
- Unexplained weight or appetite loss
- Unexplained excessive fatigue and malaise
- Swelling and pain in the left side of the belly
There is not a specific way to prevent Leukemia. However, avoidance of radiation exposure, smoking, and Benzen exposure may reduce the chance of having Leukemia.
- + Lymphoma
-
Blood Cancer that affects the immune system and especially the lymph cells which are type of the white blood cells.
Types of lymphoma
There are 2 kinds of lymphomas:
- Hodgkin lymphoma
- Non-Hodgkin lymphoma
They behave, spread, and respond to treatment differently, so it’s important for you to know which one you have.
Hodgkin lymphoma
- Hodgkin lymphoma can start almost anywhere, most often it starts in lymph nodes in the upper part of the body. The most common sites are in the chest, neck, or under the arms.
- Hodgkin lymphoma most often spreads through the lymph vessels from lymph node to lymph node.
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma
- Non-Hodgkin lymphoma is a cancer that starts in the lymphatic system in blood cells called lymphocytes. This cancer can be almost any place in the body.
- Age: People can be diagnosed with Hodgkin lymphoma at any age, but it is most common in early adulthood (especially in a person’s 20s) and in late adulthood (after age 55).
- Gender: occurs slightly more often in males than in females.
- Family history: Brothers and sisters of young people with this disease have a higher risk for Hodgkin lymphoma.
- HIV infection: The risk of Hodgkin disease is increased in people infected with HIV, the virus that causes AIDS
The most common symptom of Hodgkin lymphoma is a lump in the neck, under the arm, or in the groin, which is an enlarged lymph node.
Some people with Hodgkin disease have what are known as B symptoms:
- Fever (which can come and go over several days or weeks) without an infection
- Drenching night sweats
- Weight loss without trying (at least 10% of body weight over 6 months)
Other possible symptoms of Hodgkin lymphoma include:
- Itching skin
- Feeling tired
- Loss of appetite
Sometimes the only symptom might be feeling tired all the time.
- Age older than 60 years of age
- Men are at higher risk
- Exposure to certain chemicals and drugs: such as benzene and certain herbicides and insecticides (weed- and insect-killing substances) may be linked to an increased risk of NHL, Some chemotherapy drugs used to treat other cancers may increase the risk of developing NHL many years later. For example, patients who have been treated for Hodgkin lymphoma have an increased risk of later developing NHL.
- Radiation exposure: Patients treated with radiation therapy for some other cancers, such as Hodgkin lymphoma, have a slightly increased risk of developing NHL later in life. This risk is greater for patients treated with both radiation therapy and chemotherapy.
- Weak immune system as in AIDS and organ transplant patients
- Autoimmune diseases, in which the immune system attacks the body organs
- Specific viral and bacterial infections
- Body weight and diet: being overweight or obesemay increase your risk of NHL. Other studies have suggested that a diet high in fat and meats may raise your risk.
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) can cause many different signs and symptoms, depending on the type of lymphoma and where it is in the body. Sometimes it might not cause any symptoms until it grows quite large. Some common signs and symptoms include:
- Enlarged lymph nodes
- Fever
- Sweating and chills
- Unexplained Weight loss
- Fatigue (extreme tiredness)
- Swollen abdomen (belly)
- Feeling full after only a small amount of food
- Chest pain or pressure
- Shortness of breath or cough
- Severe or frequent infections
- Easy bruising or bleeding
There is not a specific way to prevent Lymphoma. However, avoidance of HIV infection or chemical and radiation exposure may reduce the chance of having Lymphoma.

What are the symptoms of Lymphoma - + Leukemia
-
- Leukemia is a cancer of the early blood-forming cells. Most often, leukemia is a cancer of the white blood cells, but some leukemias start in other blood cell types.
- Leukemia is often described as being either acute (fast growing) or chronic (slow growing).
- Myeloid leukemia: Leukemias that start in early forms of myeloid cells – the cells that make white blood cells (other than lymphocytes), red blood cells, or platelet-making cells (megakaryocytes) (also known as myelogenous leukemias).
- Lymphocytic leukemia: Leukemias that start in immature forms of lymphocytes are called lymphocytic leukemias (also known as lymphoid or lymphoblastic leukemias).
There are 4 main types of leukemia:
- Acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL). ALL is more common in children than in adults.
- Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). CLL mainly affects older adults.
- Acute myeloid leukemia (AML). AML is most common in older people.
- Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML)
The risk factors that put individuals at higher risk of having Leukemia are:
- Exposure to high level of radiation
- Smoking
- Exposure to Benzene which is frequently used in chemical industries and it is in the cigarettes smokes and car’s fuel (gasoline)
- Specific medications used to treat Cancer
- Specific types of bone marrow diseases
You should consult your doctor immediately if you have any of the following symptoms in a persistent (chronic) manner:
- Swollen lymph nodes (glandes) especially in the neck, armpit, and groin area
- Nosebleed, bleeding from the gum and the rectum, easy bruising, or excessive bleeding during the menstrual period
- Chills and frequent fever
- Excessive night sweats
- Bone pain
- Unexplained weight or appetite loss
- Unexplained excessive fatigue and malaise
- Swelling and pain in the left side of the belly
There is not a specific way to prevent Leukemia. However, avoidance of radiation exposure, smoking, and Benzen exposure may reduce the chance of having Leukemia.

The symptoms of Leukemia
